Metric Conversion
Instruction
Metric Conversion
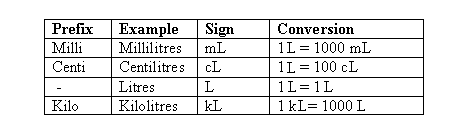
The key to understanding metric conversions is to memorize the prefixes and roots to each word. The root of each word indicates the basic measurement (litre, metre, gram), while the prefixes determine the relative size of the measurement (larger or smaller units – milli, centi, kilo, etc,).
Prefixes
All units in the metric system are easily converted because they are all based on units of 10. When converting between different measurements of the same base unit, it is as easy as shifting the decimal point. For example:
432,000 millimetres
43,200 centimetres
432 metres
0.432 kilometres
ALL EQUAL EACH OTHER
Length
Length is used to measure the distance between points. The base unit for length is the metre. The most common units you’ll encounter with length include:
Millimetres – small units (25 millimetres in 1 inch)
Centimetres – small units (2.5 centimetres in 1 inch)
Metres – larger units (1 metre = 3.2 feet or 1.1 yards)
Kilometres – large units (1.6 kilometres in 1 mile)

Volume
Volume is defined as the capacity of a given container. It usually measures the amount of liquid or gas that an object can hold. For example, the volume of a pop can is 355 millilitres, or the volume of a milk carton is 1 litre. The base unit for volume in the metric system is the litre. A litre is roughly the amount of milk that will fit into a milk carton or roughly three glasses of milk.
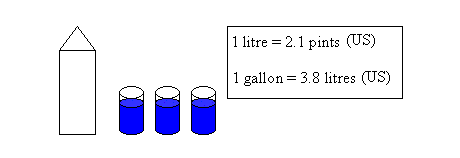
The most common prefix used with volume, is the millilitre (used to measure small amounts, such as tablespoons.) The majority of the time men measuring volume you will be using the litre measurement itself.
Mass or Weight
The base unit for weight in the metric system is the gram. The most common units you’ll encounter with length are:
Milligrams – very small (1000 milligrams in 1 gram)
Grams – small units (28.3 grams in 1 ounce)
Kilograms – large units (1 kilogram = 2.2 pounds)